1 Dec 2022
Guide to Microservices Architecture in Layman’s Language: Everything You Must Know!
Surbhi Bhatia
“We are soon going to switch to microservices architecture.”
Are you a developer?
Then you must have encountered this phrase a lot many times! But did you ever try to have a clear understanding of the concept? Why is microservices a hot topic in the context of app development?
Also Read: How to Choose a Mobile App Development Company?
Don’t worry! We are here to answer precisely what you have in mind but in layman’s language.
Yes, that’s right. So, what are you waiting for? Let’s dive deep into the ocean of information without further delay because here’s a guide to microservices for you.
Introduction to Microservices
Notably, microservices are a kind of architecture used by businesses for the development of software. Traditionally, the most common architecture for the IT industry involved Monolithic or service-oriented; however, it is no longer considered fit for the growing complexities of modern infrastructures. Thus, microservices came into the picture!
It wouldn’t be wrong to say that microservices have multiple definitions. However, one of the most commonly used is that microservices is an architectural style for developing an individual app as a software suite that’ll incorporate numerous services.
What’s more? These services are fabricated based on an enterprise’s capabilities and can be positioned independently.
The next question that most developers come up with is:
Is There Any Difference Between Microservices and APIs?
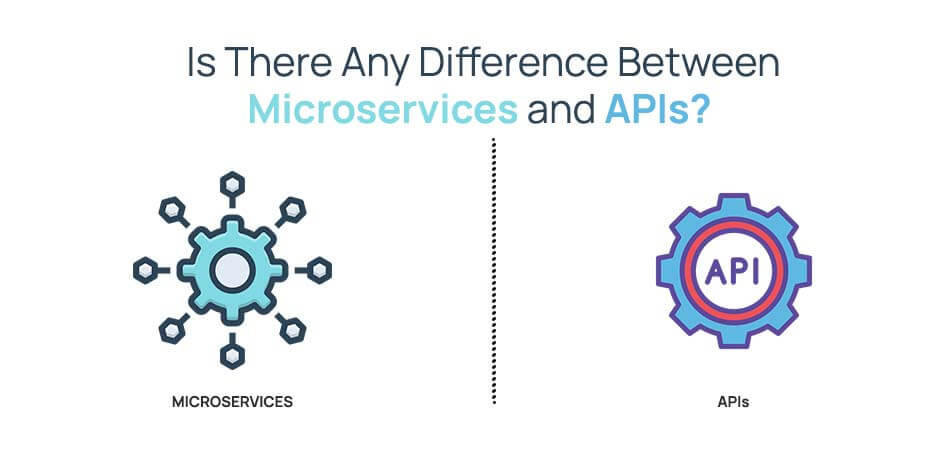
First, APIs stand for application programming interfaces, and, the two concepts are altogether different.
How?
Talking about microservices is a framework for mobile apps that segregates an app into numerous independent web services.
On the other hand, APIs are programming interface and a framework that enables a developer to interact with a mobile app. These can be arranged in a set of functions, methods, classes, and constants that work as an interface via which software can deliver its services to other software.
Where does the confusion arise?
Notably, microservices utilize APIs for communicating with each other, which causes overlap between the two concepts, leading to confusion.
Additionally, how to develop API is another commonly asked question.
Misinterpretations About Microservices
Before getting into details about the microservices architecture, a preconceived notion about the same needs to be clarified. Notably, it is believed that the term ‘micro’ in microservices denotes that the architecture only fits best with tiny services and cannot work with complex mechanisms.
Do you think this is true?
Well, it’s not! Sure, microservices comprise a small component; however, developers can effortlessly use the same for the simplest to the most complex business structures.
Another most common delusion about microservices is the assumption that it’s a new kind of protocol. However, the concept is not new, nor is it a protocol.
The Pros of Microservices Architecture
Indeed, microservices have countless advantages to offer, but it is vital for you to be familiar with the top ones. Hence, here’s the list:
1. Lower Development Time
The credit goes to distributed development that enables developers to emphasize multiple microservices simultaneously. Therefore, the development time of an application reduces as several developers come together to work on a project without interfering with each other’s production.
2. Enhanced Scalability
Microservices are independent of development and deployment; thus, developers can refurbish a component without influencing other components. The result? It enables mobile apps to evolve and meet the dynamic demand, eliminating any disruption.
3. Decreased Downtime
Contrary to monolithic apps, a mobile app built using microservices architecture doesn’t stop working when an individual component encounters an issue. Not only this, but it becomes less complicated to monitor and fix issues in this ecosystem.

4. The Versatility of Each Microservice to the Working Tools
The independent components make it possible to construct microservices using varied programming languages. This is why the operational tools utilized by an organization are fit for the global solution.
Four Layers of a Microservices Ecosystem
It won’t be wrong to say that the microservices ecosystem is massive and needs a tremendous infrastructure. Thus, developers must begin working from scratch, and not compromise with the same as it works with a dedicated environment.
The implementation has to be positive, and to ensure the same; sustainability is a must-have ingredient.
So, how to move ahead?
Listed below are the best practices for a microservices environment:
1. Hardware
This microservices layer incorporates databases, OS, and physical host servers. No matter Windows, Solaris, or Linux, the OS must utilize a configuration management tool; for instance, Puppet or Chef. Additionally, it must be the agent that installs applications and defines configurations, or else, scalability issues might arise.
For scaling, the cycle of configuration has to be repeated, and host-level monitoring will be required for troubleshooting issues that encounter.
2. Communications
Notably, this microservices layer influences all other layers of the ecosystem.
How?
In the absence of a proper interaction, other components of the architecture stop working. For example, talking about data, microservices can utilize HTTP and RAF or a TIFF communicating channel. For messaging, the ecosystem can forward messages using HTTP or another chosen protocol.
3. Development
This phase comprises the development of applications, and it is mandatory for this layer to host the self-service development tools for the creation of new databases, ports, tables, and more. Furthermore, the amalgamation of logging and monitoring tools is a crucial stage in the development layer.
4. The Microservice
The last and simplest layer is the microservice, where the entire mechanism runs. Here’s precisely where the configuration file lives and where the self-service tools from other layers should be placed.
Undoubtedly, the architecture is becoming exceptionally popular, and it has become one of the top-notch reasons for businesses to adopt the functionality for app development and cloud microservices.
Also Read: Cloud Computing in Healthcare
In a Nutshell
Constructing a microservices architecture demands the right expertise and technical skills. Not only this, but it also requires a transition in the manner that you conduct your projects internally.
So, do you want to reap many benefits offered by the microservices mechanism?
It’s time to reach out to us at Techugo- a reliable mobile app development company for further guidance on the subject!
What’s more?
Visit the Youtube link to listen from our industry expert:
If you’re on the journey to developing an applaud-worthy mobile app for your business and are wondering about the investment, also read- Cost to Develop a Mobile App!
Happy innovation!
Get in touch.
Write Us
sales@techugo.comOr fill this form



 SA
SA  KW
KW  IE
IE AU
AU UAE
UAE UK
UK USA
USA  CA
CA DE
DE  QA
QA ZA
ZA  BH
BH NL
NL  MU
MU FR
FR