Write Us
We are just a call away
[ LET’S TALK AI ]
X
Discover AI-
Powered Solutions
Get ready to explore cutting-edge AI technologies that can transform your workflow!

Businesses can use various programming options, but knowing your company’s goals and requirements is crucial to selecting the right solution. If you are considering developing software for the enterprise, you must understand what robust enterprise software development means and how it differs from standard software development.
Robust enterprise software development has been the foundation of digital strategy. Companies that invest in this development achieve higher operational efficiency and competitive advantages.
Have you ever wondered how large companies and organizations manage their operations and how they can provide the best customer experience? The answer lies in their ability to design corporate software that meets their requirements. Let’s learn how this game-changing technology improves workflows, speeds up decision-making, and allows companies to expand like never before.
Enterprise Software is the generic term for applications designed for large organizations or enterprises. It is customizable to help with tasks in different functions, including marketing, HR, finance, health supply chain, and customer relationship management (CRM). Contrary to the standard software that customers use for businesses, custom software concentrates on scalability, reliability, and integration with other systems.
Ultimately, developing enterprise-level software is a tried-and-true method of boosting operational productivity and efficiency through business software’s security, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Business process automation is the core of enterprise software. It helps streamline operations by utilizing workflow engines that manage tasks’ routing and approval processes. Advanced document management systems ensure efficient information flow. Customized reporting tools and performance monitoring dashboards give real-time information about the effectiveness of your operations.
Seamless system integration allows for a seamless flow of information across the entire organization. API management systems allow external connections. An Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) architecture assures secure communications between systems.
Custom connectors bridge gaps between different platforms. Integrations between legacy systems preserve important old information. Microservices architecture offers the flexibility and ability to scale.
Modern enterprise software consists of various interconnected parts. Each plays a crucial role in creating a comprehensive solution that is the basis for a business’s success. Understanding these components can help companies develop their growth strategies effectively.
A well-organized data management system is essential for making informed decisions. Centralized data repositories are one source of information for organizations’ data. Data warehouse solutions allow for sophisticated analysis and reporting.
Real-time analytics capabilities power quick decision-making. Custom ETL processes ensure accuracy and accessibility. Data governance frameworks guarantee the quality of data and ensure compliance.
Robust security measures protect businesses’ essential assets. Role-based access control allows for appropriate access to data, and security frameworks for encryption protect sensitive data. Audit log systems monitor system use and adjustments. Compliance monitoring tools ensure compliance with regulations. Systems for responding to security incidents allow rapid threat mitigation.
Enterprise software, also known as Enterprise Application Software (EAS), is designed to meet the particular requirements of large-scale companies, in contrast to other software designed for general use. It is a complex set of business processes, such as sales and commercial documents.

The main goal of this initiative is to provide various additional tools and features made specifically for facility and corporate workflows. This could include features that only an employee could use. A company is the ultimate user of an enterprise software program, while the person-user is the ultimate software user for general use.
In addition, the number of users using business software is significantly lower since it’s intended to support only the company’s employees with various tasks and roles, allowing them to complete their assignments on the shop floor. However, the feature set of these software solutions is much longer because each department and every worker is assigned a specific role in the complicated enterprise structure.
Contrary to enterprise software, standard solutions are generally generic. They do not have a limited focus and target audience; they are being designed to meet the needs of everyone. They’re accessible on personal devices and operated exclusively by ordinary users whose professional duties aren’t essential. Examples of typical software include entertainment apps, education apps, and communication tools.
Since the users who use the software are not part of the development of commonly used software, they aren’t able to influence the development process directly through their input. The developers decide on the features, design, style, and UX list.
These two kinds of software are designed to meet different goals and are tailored to other environments. This is evident in their development strategies and methodologies. In addition, whereas common-purpose applications and programs tend to be designed in a single, wholesome way, enterprise software is always flexible (for integrations or connections, etc.). Let’s take an in-depth look.
There is a variety of ERP software available online. With robust enterprise software development services, businesses can build mobile enterprise applications, web applications, and cloud-based native apps that meet their specific requirements. These tools help companies to operate efficiently, reduce time, and develop faster.

Web-based corporate applications are specially designed tools that work with your browser. You can access them from any device that is connected to the internet. They use cutting-edge technologies like AI and IoT to help you work smarter. Imagine having a super-smart assistant on your computer! The software development lifecycle (SDLC) is the step-by-step process of creating these software applications.
Employees can use the apps simultaneously, regardless of whether they are in different places. If an app needs to be updated, it is a simple process. The updates are performed on massive servers or computers. Everyone then receives the new version immediately. Machine learning helps these applications get more intelligent with time. Developing enterprise software products for web-based applications requires a flexible approach to ensure regular updates and seamless user experience. It’s like watching your work tools evolve with you. They facilitate collaboration between everyone!
Mobile apps for corporate use simplify work for company employees. These apps work with tablets and phones and allow workers to perform their jobs from anywhere. Imagine a salesperson meeting a client’s needs. They can immediately update customer information right through their iPads. The app is run by continuous app management, which ensures that everything runs smoothly.
Companies start with MVP development for enterprise applications to determine what works best. It is a matter of beginning with a basic version and then enhancing it. The apps connect to the company’s system instantly. The information is kept up-to-date. Everyone within the company can view the latest updates. This makes work more efficient for all employees. These apps are similar to having an office in your pocket!
Cloud-native software is a specialized program that runs on the cloud. It is designed using cloud-based software development techniques to run optimally online. Major corporations like Microsoft and AWS help create these applications through agreements with industry players. Consider the cloud to be a considerable computing system in the sky!
The apps can grow or shrink based on the quantity you’ll need. They are incredibly flexible. Businesses only pay for the services, like switching off the lights when leaving the room. Cloud providers are accountable for ensuring that everything is safe and functioning.
Your company’s technical team is not liable for issue resolution. The apps make tasks easier and also save money. Software developers for enterprises focus on cloud-based applications that offer flexibility, scalability, and efficient infrastructure management for companies of all sizes. It’s like having a magic toolbox that’s always the right size! Software development for businesses encompasses solutions such as ERP, CRM, and cloud-based software that can help companies to reduce their processes and boost the quality of their decision-making. Enterprises developing enterprise-level software must consider Cloud compatibility, data security, and integration with other systems.
Making enterprise software can be like building a house. You start with a plan, build solid foundations, select the appropriate substance (technology in this instance), and then you can create spaces (features in this instance).
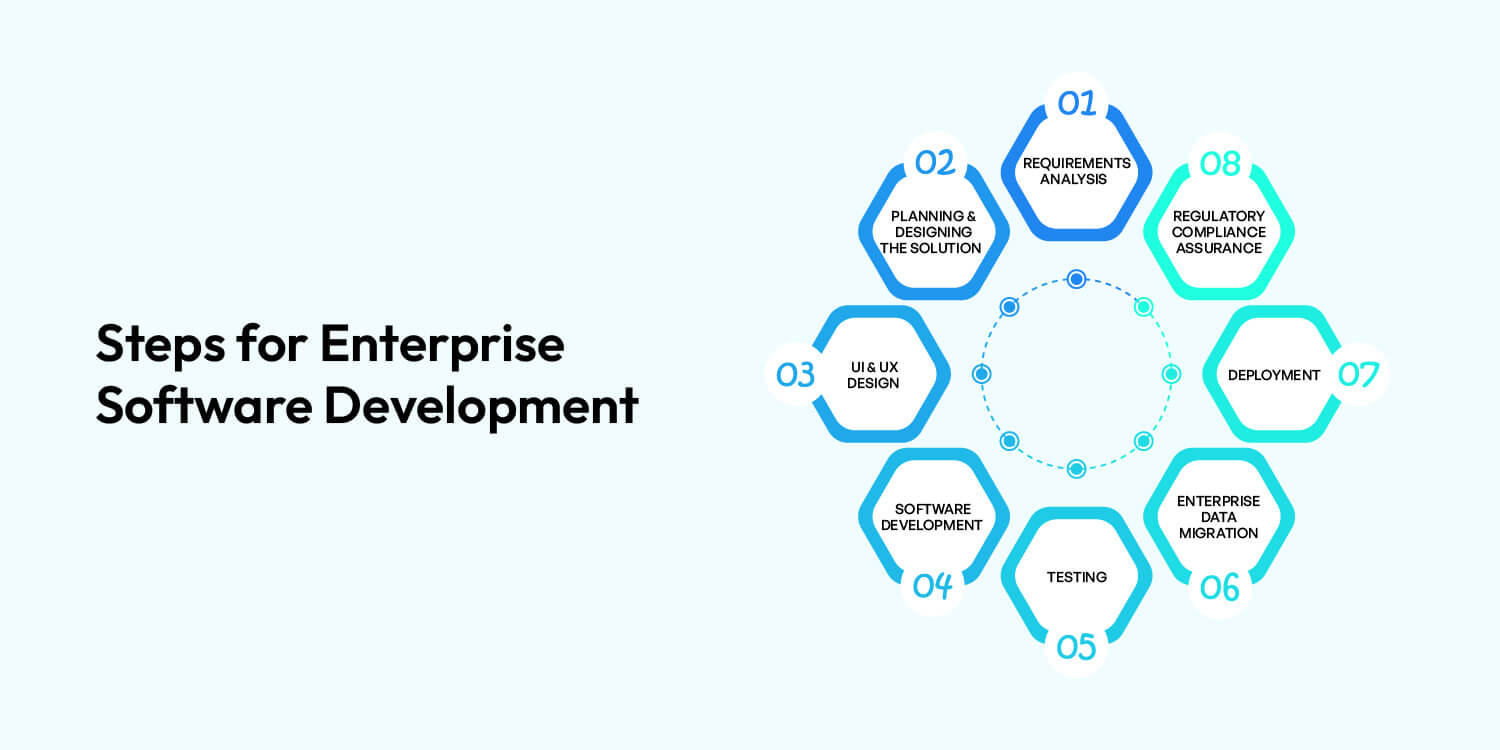
Here are the most critical steps in the process of developing enterprise software.
In this phase, the tech consultant can work with your team to understand your company’s goals, requirements, and issues. They seek to establish the software’s purpose and capability to solve problems, talk with critical stakeholders, and guarantee that it is feasible. This stage involves various activities, such as documenting business procedures, analyzing IT capability, and analyzing broad business strategies, such as expansion and IT budgets. These elements affect the design and technology choices. The technical and functional requirements of the application are defined to set the foundation for future development.
Furthermore, the requirements analysis evaluates possible risks associated with implementing the new system, including the loss of productivity and downtime when transitioning to digital workflows and user training. The thorough process results in a clearly defined plan and road map throughout this development phase.
At this stage, the team will outline the roadmap for software development projects, including goals, budgets, and other assignments.
The Project Manager, Business Analyst, and Project Owner work together to study the market, competition, and the project’s requirements, typically leading to the first MVP. The System Architect then focuses on software architecture and the user’s experience from the end user’s perspective, which includes enterprise applications, integration, and architecture design. Prototyping is a crucial aspect. The process also includes designing the architectural style, tech stack, and development process, focusing on the next phase: UI/UX design.
Furthermore, data flow and transformation protocols, communication protocols, and security enhancements are identified.
The team reviews a complete QA plan to confirm the system’s interactions with Backup and recovery mechanisms and their performance within the bandwidth limits.
Designing a User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) for an enterprise application must be a well-thought-out and user-centric procedure.
In this phase, UX designers and Business Analysts collaborate to conduct UX research. They will examine the intended audience’s requirements, objectives, and mental representations. UX designers sketch user interaction and information architectures while determining digital points of contact.
Wireframes are created to show the layout of content and its functionality, and then they are combined into a prototype application to be tested. Following successful prototyping, UI designers convert them into vivid mockups of interfaces ready for the front-end developer to use.
At this point, the developers bring the software to life by writing code according to the requirements and design. Back-end developers take care of the inner operations, employing the selected technology stack to develop the software, which includes functionality, database connectivity APIs, and seamless integration with other business applications.
Frontend developers are focused on user interfaces, using HTML5/CSS3 and JavaScript to design visually appealing elements with which users can interact. Integrating databases and systems is crucial to ensure seamless data flow and cohesion with other tools.
This stage transforms the project plan and design into a reliable, functional software solution that aligns with your business goals.
A rigorous app testing process ensures the software fulfills the specified specifications and performs as designed. The QA team runs various tests, such as functional tests to confirm the software’s intended functions, usability tests to ensure the user’s experience, and performance tests to test the software’s effectiveness under various situations.
Security testing also protects enterprises’ data, while testing for compatibility guarantees seamless performance across various operating systems and gadgets. Software testing is an iterative process, with the results leading to needed adjustments and testing again.
Testing ensures that the enterprise software performs as expected and meets the organization’s requirements.
Data from existing systems and other sources is transferred into the software during data migration in robust enterprise software development.
This ensures that all historical data, user details, and essential information about business transactions are effortlessly incorporated into the new system.
Here’s what you must do at this stage:
This is an essential step in developing software for enterprises, which marks the transition from development to use in real life. During this stage, a series of crucial steps are performed:
The deployment phase ensures the software works properly within the company’s operational environment.
You must check that your software complies with industry or government regulations, like HIPAA, CGMP, GLBA, PCI DSS, or GDPR. Make sure you follow these steps:
This is essential to ensure that the industry complies with government regulations.
Have you heard that over 80% of businesses believe that custom enterprise software development tools give them an edge over competitors? Let’s find out how to locate a custom enterprise development firm that is the best option for creating an enterprise-grade software program for your business.

Another essential aspect to consider is the flexible scaling of a team’s size according to demand. A reputable company that offers custom software development in Dubai will determine the size and composition of the team according to the project’s current needs. This gives you the appropriate resources at the right moment and optimizes cost and efficiency.
If the project’s requirements require speedier development or more efficient operations, the ability to scale flexibility significantly impacts the project’s performance.
A dependable ERP service provider can ensure that your ERP system complies with the security standards for data (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.) and enhance its digital protection. They provide secure encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to protect sensitive business information. Additionally, your trusted development partner is always up-to-date on the latest laws and regulations to ensure your system can adapt to the changing industry requirements. This proactive approach reduces risk and ensures your business operations are safe and stable.
One of the most important aspects is the company’s industry knowledge. A service provider with experience in your field makes the right choice when comprehending your needs and challenges. Their expertise in developing enterprise software can be found in client reviews and testimonials, highlighting their knowledge and expertise in the field. In addition, it guarantees their ability to handle projects similar to yours.
Scalability and quality of the enterprise software are the most important factors when choosing a development partner. An experienced and reliable development partner complies with the highest quality standards, using rigorous testing and quality control methods to offer high-quality and secure solutions.
Furthermore, enterprise software must be scalable, meeting businesses’ ever-changing requirements. This is essential to ensure long-term success. The software must handle more functions and increased workloads without impacting efficiency.
Today, new trends such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and RPA (Robotic Process Automation) are getting more attention. These technologies help reduce the cost to develop a software in Dubai and adapt to changing business requirements. We’ve listed the most critical enterprise software developments below to help decision-makers improve productivity, drive modernization, and streamline the efficiency of business processes.
Let’s examine them one at a time.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is among the most important developments you must hear about, especially in modernizing custom software development for enterprises. RPA tools automate rule-based routine tasks by mimicking human-computer interactions in software systems.
It is advantageous to use RPA to automate data entry, report generation, workflow automation, and invoice processing. Additionally, RPA adoption to develop enterprise software will expand over the next few years as more businesses focus on streamlining time-consuming business processes.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are increasingly popular as companies develop them using customized enterprise software. Manufacturing, healthcare, and retail are a few industries using AR and VR capabilities that go beyond flat-screen displays and personalized notifications.
Implementing AI and ML in enterprise software allows companies to implement intelligent chatbots that offer instant interaction. Based on AI-generated suggestions, user experiences will be more personalized and will be able to forecast market trends. This will further improve processes and repetitive tasks and create new ideas.
Thanks to low-code or no-code mobile app development in Dubai, business owners and experts in their field can explore new ideas and innovative concepts without putting in the effort and time of skilled developers. Additionally, companies can offer clients the ability to modify the user interface and software components.
Reliable enterprise software has various benefits vital for those who want to remain relevant and competitive in today’s digital marketplace. This includes:
Monotonic tasks are a significant problem for any business. Enterprise software can automate data entry, create reports, and automate other tedious processes. This lets you and the team concentrate on more strategic goals, including securing new markets or developing innovative products.
Modern companies always look for ways to increase their investment returns (ROI). Enterprise software assists them in streamlining processes, reducing mistakes, and optimizing resource allocation. This leads to cost savings in productivity and, ultimately, a better bottom line.
Do you remember the time you spent trying to get approvals or rummaging through spreadsheets for the most basic details? Enterprise-grade software can automate these processes and integrate various information sources across departments. It facilitates seamless workflow within a business environment, improving operational efficiency and decreasing team friction.
Have you ever felt like the information you need to collect is scattered across different departments, making it difficult to understand your business’s health? This is why enterprise software functions as a central repository, offering a comprehensive view of key business metrics across the organization. It helps ensure all employees are on the same page, which allows them to make informed decisions and create an environment of open and transparent communication.
The most precious resource is time. In business, enterprise software can be your time-saving superpower. Streamlining workflows and automating tasks eliminates bottlenecks and keeps your business operating like a well-oiled machine. This lets organizations achieve more quickly, which allows you to relax and concentrate on the things that matter, such as growing your business.
In today’s speed-first economy, enterprise software development is undergoing significant changes. In the wake of changing market requirements and technological advancements, several drivers are determining what’s to come in this field. Let’s look at a few of the essential drivers and analyze the impact they have on us:
Change is a possibility and is embraced by the technology industry due to improved methods and enhancements that will stay relevant in the future. With the shift in the development environment, the transformation of IT in the enterprise. Instead of being primarily tech-focused, the software is analytical-heavy. Enterprise Software is becoming more user-friendly by providing distinct modules for specific, drastically customizable features. The development of enterprise applications is a continuous process that continues to evolve. What is the real improvement?
Artificial Intelligence has long been setting trends in enterprise software. Even the enterprise software industry makes software technically viable by using smart data to make the most intelligent decisions.
However, implementing automation in every software detail can ensure robustness, scalability, and security. Machine learning technology and IoT are pushing corporate data to be innovative and respond intelligently while increasing the totality of software for corporate use.
Every business must evolve in the age of digital technology to establish web-scale IT standards since there is no room for a lean patch! No one is out of the loop because enterprise IT is advancing fully. Organizations of all sizes must compete and be ready for the storm. Old systems must be upgraded to allow IT companies to alter vital applications by filling them with feature-rich content. For that, trusted enterprise-level mobility management partners such as Techugo play a significant role.
The re-designing of enterprise software makes it more accessible as a program, even though it undergoes significant turnover.
In the past, we’ve examined a few issues regarding projects developing enterprise software. We know that enterprises implement their tools in different environments. With this in mind, we can delve into some of the more particular operational, technical security, and other issues developers face.

It is a given that security is the most crucial factor when it comes to enterprise software. But what exactly does this mean in terms of practical application? Initially, it is essential to clearly define and manage the level of data disclosure we intend to give to every type of user.
We need methods for verifying and authenticating user identities to stop unauthorized access. Of course, security in the enterprise is more extensive than this. In addition, you’ll generally see other levels of protection, such as on an infrastructure level. This is a reason why self-hosting is an essential feature of enterprise-grade solutions.
Vendor lock-in happens when businesses depend on a specific system or provider, exposing them to unnecessary costs such as price increases, end-of-support, or other undesirable adverse effects. For example, if you used the ERP platform on which a significant portion of your business relied, it could be an issue if the vendor raised their price by 20 percent.
Of course, this is a convincing argument for custom-built builds. However, we may be confronted with vendor lock-in in other ways. For instance, you can use an external contractor or specific tools to develop and maintain your systems.
We’ve mentioned before that larger companies aren’t always quick compared to smaller companies. One area where this is most evident is the introduction of new tools and platforms. Change management, therefore, can be a complicated issue for projects involving transformation.
Internal barriers that hinder change may be a particular issue. They can result from employees’ resistance to a lack of support from top decision-makers. In addition, we could face problems with dependence on existing systems and difficulties in developing new solutions that do not compromise the existing ones.
We’ve already discussed how it is essential to know how our build will affect user management’s workload when we build a custom system. The IT team has enough to do without having to contend with the burden of admin tasks.
Much more than smaller businesses, enterprise software development needs to make efficient administrative workflows the core of the decision-making process.
We must also be aware of the complexities of the regulatory framework that businesses operate within. We can consider this on various levels. One is that international trading organizations are inherently more likely to encounter differing or contradictory regulatory requirements across jurisdictions. This is similar to the way the current data protection regulations can result in higher standards or derived requirements for particular categories of data, such as individuals who are data subjects or processors.
We also deal with non-legislative instruments such as industry-specific certificates or internal controls. One major issue is that we shouldn’t expect developers to be compliance experts. We’re left with a better option of putting out clearly defined processes and software stacks that are approved to take away the discretion to make the compliance-related decisions of developers in the sense that it’s possible.
There are also internal processes for legal and financial matters to manage. Reviewing agreements and suppliers for any outside partner is an arduous task. This is particularly problematic regarding software since there is a greater need to react quickly.
This could restrict IT teams’ choices regarding responding to changing demands or new challenges. It also gives more emphasis on internal builds because we don’t need to think of vendor contracts. Open-source development also plays a significant role in this regard, as it helps to solve some of the operational problems that internal processes are meant to tackle, including vendor lock-in.
This is the definitive guide to streamlining your business software development initiatives. By following these steps, you’ll enhance your enterprise web software development results and increase the efficiency of your employees by ensuring top-quality software solutions. To summarize, successful enterprise software development depends on adherence to precise design principles, development procedures, testing strategies, and the importance of maintaining and deploying.
Adhering to scalable architecture with robust integration and agile methods allows enterprise mobile app development company in Saudi Arabia to develop software that can meet the changing business requirements and technological advances.
Prioritizing these aspects, like testing for security, functionality, or performance, will provide top-quality solutions. However, careful deployment and ongoing support will increase user satisfaction and acceptance.
If you are looking for a trusted partner to build top-tier enterprise software, hire Techugo for cutting-edge solutions that drive efficiency, scalability, and success. Get in touch today.
Write Us
sales@techugo.comOr fill this form