Write Us
We are just a call away
[ LET’S TALK AI ]
X
Discover AI-
Powered Solutions
Get ready to explore cutting-edge AI technologies that can transform your workflow!

“My app/website is beautiful, but when Arabic-speaking users open it, the interface looks confusing to them. Text alignment looks weird, navigation seems upside-down, and the overall flow feels chaotic.”
Do you face the same issue?
Well, this is an everyday problem of many businesses that don’t get a proper UX audit of the Arabic interface. As we know, Arabic is read from right to left, which means that design principles good for English or French don’t always translate seamlessly. This problem needs a proper solution, i.e., a UX audit for a right-to-left interface. And businesses that ignore it, especially in markets like Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, are frustrating their core users and ultimately losing revenue.
To learn the common reasons behind users’ frustration, and what could be the possible steps on how to conduct a UX audit for Arabic right-to-left interfaces, keep reading this blog.
Designing for Arabic users is different from designing for English speakers. A simple copy-paste of layouts does not work. Moreover, there are some cultural considerations in Arabic UX audits that need to be considered. This is why a UX audit for Arabic interfaces becomes so important. Let’s see some challenges:
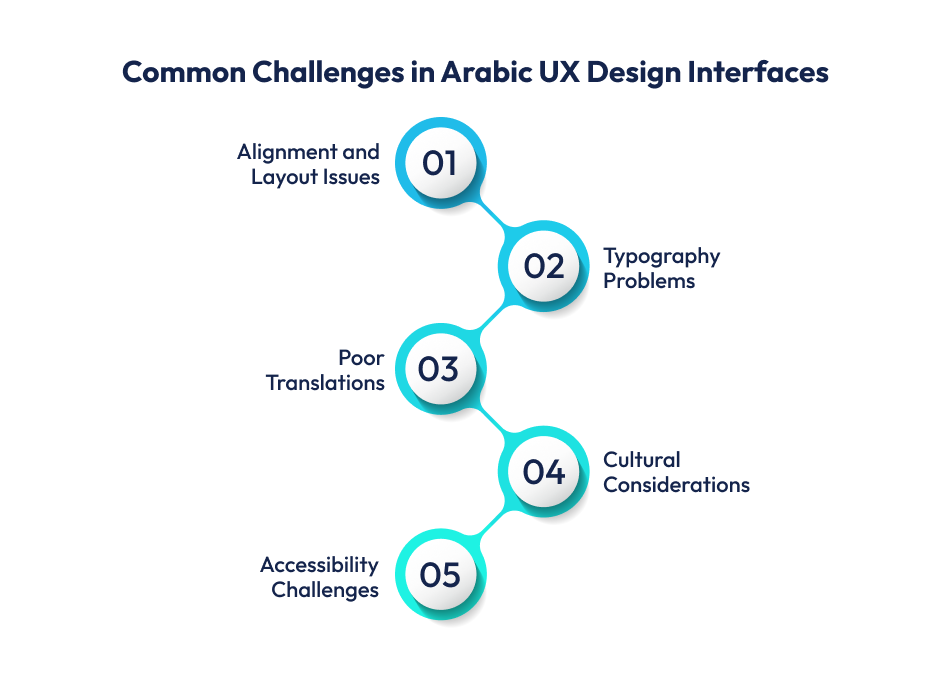
Arabic is read from right to left. Many global templates are built for left-to-right languages. When the design is mirrored, buttons, icons, and menus often look misplaced. For example, a shopping app may show the “Add to Cart” button on the wrong side, confusing users.
Arabic fonts have a flowing, cursive style. If the font is too small or not supported by the system, the text may appear broken or squished. This makes it difficult for users to read product details or instructions clearly.
Direct translations don’t always work in Arabic. Words may lose meaning or context. Imagine a banking app where “transfer” is translated poorly, it can cause serious misunderstandings.
Design is not just visual; it’s cultural. Cultural considerations in Arabic UX audits include colors, symbols, and images that may have different meanings in their culture. A color used for “success” in one culture might signal “danger” in another. If designers miss this, the interface can feel unfamiliar or even offensive.
Accessibility in Arabic UX design is often overlooked. Screen readers may not work well with Arabic text, and contrast issues make it harder for elderly users to read. For example, if a health app uses light gray text on a white background, users may struggle to follow instructions.
These challenges show why a UX audit for Arabic interfaces is essential. It helps identify design flaws, cultural gaps, and usability problems before users face them. Let’s jump into how to overcome these challenges in RTL UX interfaces.
If you are running a business in Saudi Arabia or the UAE, your website or app must feel easy and natural for Arabic-speaking users. A UX audit for Arabic interfaces helps you check if your design truly works for right-to-left reading.
Let’s divide it into 5 simple and practical steps –
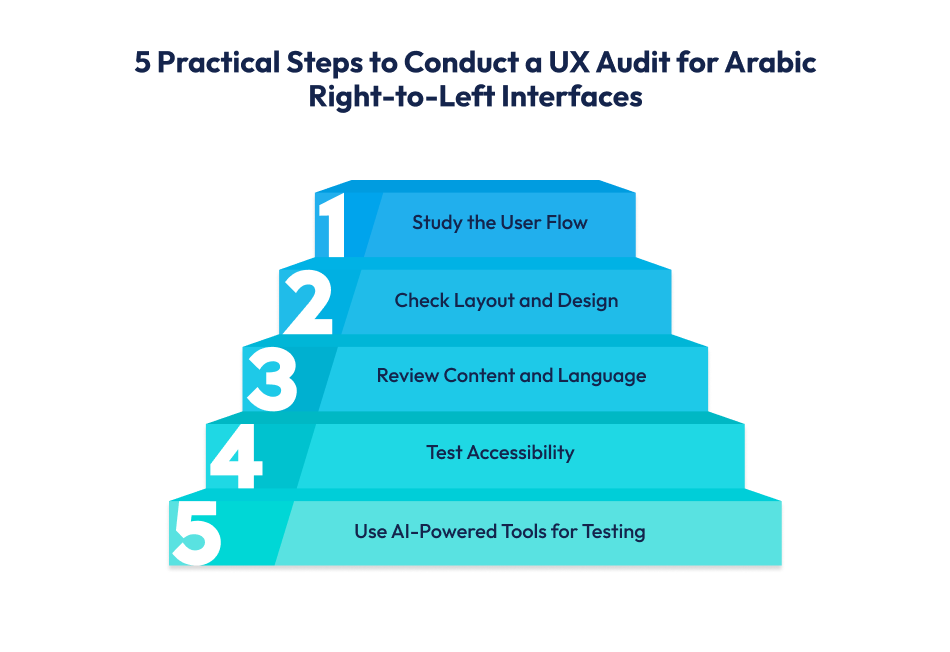
The first step in any UX audit for Arabic interfaces is to walk through the app or website exactly like your user would. If they are an Arabic speaker in Riyadh or Dubai, you need to experience their perspective.
“User Flow = Onboarding and Sign-Up > Navigation Flow > Checkout and Payment”
A user flow means the path a person takes to complete an action, such as signing up, buying a product, or booking a service. In a right-to-left UX audit, this path must feel natural and smooth for Arabic users.
Here’s what we look at closely:
If your customer can move smoothly from start to finish, they stay happy and complete their journey. If not, even a small glitch, like a misplaced button, can make them quit. That’s why a UX audit in UAE and Saudi Arabia must start with the user flow.
Ensure flawless user journeys with a mobile app development company in Dubai that understands Arabic UX design. Schedule a free call today!
After studying the user flow, the next step in a UX audit for Arabic right-to-left websites and apps is to carefully examine the layout and design.
Why? Because Arabic readers process screens differently from English readers. If your layout is not adjusted, users may feel lost or frustrated.
Here’s what an Arabic UX auditor usually looks at:
Arabic text flows from right to left. That means –
Important buttons, like “Next” or “Submit,” should sit where the Arabic eye expects them, on the left side (opposite of English layouts).
b. Fonts and Readability:
Arabic fonts behave differently than English fonts.
c. Icons and Visual Direction:
Icons carry hidden direction. In Arabic UX design:
Arabic script often takes more space than English. Words stretch, and lines wrap differently.
A Saudi banking app, for example, displayed transaction details in both English and Arabic. But Arabic text got cut off in buttons. The mobile app UX audit suggested flexible containers, so all words fit properly.
Design isn’t only about fonts and buttons. Visuals must also feel relevant.
In short, Arabic UX design audits always test layout and design in detail. Even small mismatches, such as flipped arrows or unreadable fonts, can break trust. When the design “speaks” Arabic, users feel at home and are more likely to engage.
Even if your layout is perfect, the content and language can still make or break your product. In a UX audit for Arabic interfaces, this step is about checking how the words, tone, and translations work for your audience in Saudi Arabia, the UAE, or any Arabic-speaking region.
Here’s what matters most:
Arabic is not just a “switched version” of English. Direct translations often sound robotic.
For example, an e-commerce app translated “Checkout” as “خروج” (which means “Exit”). This confused buyers, who thought they were leaving the app. After the Arabic UX optimization, it was replaced with “إتمام الشراء” (Complete Purchase), which made sense.
Arabic has different tones depending on the region and audience.
For example, a fintech app in Riyadh used playful words like “هيا بنا” (Let’s go). Users found it unprofessional. The UX audit in Saudi Arabia suggested formal alternatives, which matched customer expectations.
Arabic sentences can be long. But in UX, short and clear text works best.
For example, a Dubai fitness app had a button saying “Start التمرين” (mix of English + Arabic). Some users didn’t understand it. After revising to just “ابدأ التمرين” (Start Workout), usability testing showed fewer errors.
Check if terms are consistent across the app or website.
Many users in the UAE and Saudi Arabia switch between Arabic and English.
For example, a Saudi shopping app crashed when switching from Arabic to English because labels overlapped. The UX audit for right-to-left interfaces fixed this with responsive design rules.
So, reviewing content and language is not just about fixing typos. It’s about localization, clarity, tone, and cultural respect. A well-written Arabic interface makes users feel the product was built for them, not just translated.
Accessibility is one of the most overlooked parts of a UX audit for Arabic right-to-left interfaces. But in markets like the UAE and Saudi Arabia, where apps are used by people of all ages and abilities, ignoring accessibility can mean losing a big chunk of users.
Here’s what an Arabic UX auditor checks:
Arabic users who rely on screen readers face challenges if apps aren’t built properly.
For example, a government app in Riyadh had a “Download Form” button, but the screen reader read it as “Button, no label.” After the Arabic UX design audit, clear labels were added like “تنزيل النموذج,” helping visually impaired users navigate smoothly.
Accessibility isn’t only about sound. It’s also about what users see.
For example, a health app in the UAE used light grey text on a white background. Older users couldn’t read instructions. The UX audit for Arabic interfaces suggested darker fonts, which improved readability instantly.
Arabic words are often longer, which can push buttons close together. That makes it hard for users with motor disabilities, or even someone in a hurry, to tap the right option.
For example, a Saudi banking app placed “Send” and “Cancel” buttons side by side. Users sometimes hit the wrong one. After the mobile app UX audit for Arabic users, spacing was increased, reducing mistakes.
Accessibility also means designing for different devices.
For example, an e-learning app in Dubai broke its layout when students zoomed in on Arabic text. A UX audit with AI-powered tools helped test multiple devices, ensuring all screens scaled properly.
Accessibility is technical, and cultural too.
For example, A lifestyle app used a “thumbs up” emoji as approval. In some Middle Eastern cultures, that gesture can be misinterpreted. The cultural UX design audit recommended replacing it with “✔️ موافق” (Approved), which worked better.
Accessibility testing ensures your product isn’t just usable for some people; it’s usable for all Arabic-speaking users, including those with disabilities, older age groups, and diverse cultural backgrounds. Skipping this step can cost trust and adoption in both the UAE and Saudi Arabia.

In modern UX audits for Arabic right-to-left interfaces, AI is just wonderful. It helps spot issues faster, predict user behavior, and even suggest fixes. These are the things a manual audit might miss. Using AI in Arabic RTL interfaces makes your app smarter, smoother, and more user-friendly.
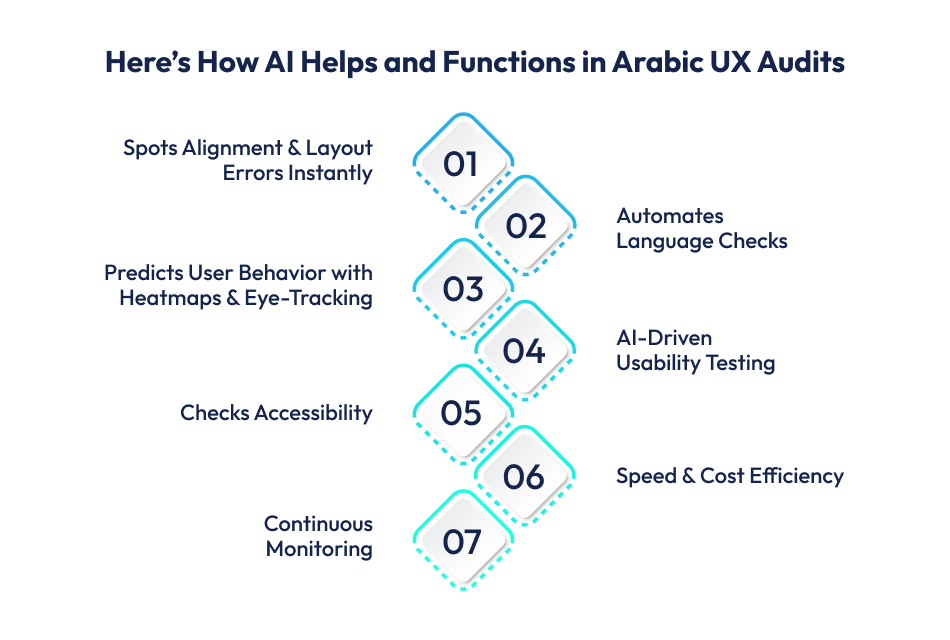
Here’s how AI helps in detail:
AI can track where users tap, scroll, or get stuck. This shows exactly which parts of the app or website confuse Arabic users.
AI can predict potential problems before real users encounter them. It simulates Arabic-speaking user behavior and highlights areas that may cause friction.
With AI-powered UX audit tools, Arabic text can be checked for proper alignment, wrapping, and readability. It ensures no words break awkwardly or overlap UI elements.
AI can record user sessions and analyze them automatically. You see exactly how Arabic users navigate the app – which buttons they click, where they pause, and where they get frustrated.
AI can simulate multiple devices and screen sizes to ensure Arabic RTL layouts work everywhere. It also tests contrast, font size, and screen reader compatibility.
Using AI in UX design, especially for Arabic apps, saves time, reduces errors, and ensures your product meets user expectations in the UAE and Saudi Arabia. It complements traditional auditing methods, making your UX audit for right-to-left interfaces more precise and actionable.
If you’re looking for expert UX testing for Arabic-speaking users in Dubai, let Techugo guide your audit process. Message us today!
Conducting a UX audit for Arabic interfaces is complex. Right-to-left (RTL) layouts, cultural nuances, language variations, and accessibility needs make the process far more detailed than standard audits. Manual audits are helpful, but they are time-consuming and prone to human error. This is where AI in UX design changes the game. AI speeds up the process, and adds precision, consistency, and deep insights that human teams may overlook.
Here’s how AI helps, step by step, even in the smallest details:
In a manual audit, designers must check every screen for alignment, such as – text, buttons, icons, and navigation bars. This takes hours, sometimes days.
Arabic words are often longer than English ones, which can cause text cutoffs or wrapping issues. Manually spotting these across devices is nearly impossible.
AI does review static layouts, as well as predicts how Arabic users interact with interfaces.
Traditional usability testing requires hiring testers, recording feedback, and analyzing results manually. That takes weeks.
To expand across UAE & Saudi Arabia with seamless RTL UX, get in touch with Techugo, a leading mobile app development company in UAE.
Accessibility is tough to test manually because it requires checking contrast, fonts, voice-over compatibility, and screen readers. AI makes this easier.
For example, an e-learning app in the UAE used AI accessibility testing. It found that the Arabic “Back” button wasn’t read by screen readers. Fixing it improved inclusivity for visually impaired students.
A manual UX audit might take weeks, especially for apps with dozens of features. AI compresses this timeline.
For example, a UAE-based delivery app integrated AI audits into their workflow. Each new app update was automatically tested for RTL issues before release. This saved them both money and reputation.
UX audits aren’t one-time tasks. Every new feature, translation update, or design tweak can introduce errors.
With AI in Arabic UX audits, businesses save time as well as gain accuracy, cultural sensitivity, and scalability. Every minor issue gets flagged before real users ever face it.
This is why AI is becoming the backbone of UX audits for right-to-left interfaces, especially in regions like the UAE and Saudi Arabia.
Having a good understanding of cultural, linguistic, and design depth is crucial for UX audit for Arabic right-to-left interfaces. Team at Techugo doesn’t just “translate” apps or websites; it rethinks the entire user journey for Arabic-speaking audiences.
Our team specializes in UX audits for right-to-left interfaces and guarantees proper alignment, layout, and navigation flow. We conduct cultural UX design audits to check if visuals, icons, and metaphors resonate with local audiences.
We integrate AI in UX design to speed up audits and maintain accuracy, as AI helps us spot issues faster. Moreover, we ensure your product works for all Arabic-speaking users, including those with visual or physical challenges. Our UX audits with AI cover screen readers, contrast checks, and device testing.
Since user expectations differ by region, so, in the UAE, bilingual support (Arabic + English) is critical. In Saudi Arabia, formal Arabic tone and cultural sensitivity play a bigger role. Thus, we adapt your product to fit both markets perfectly.
A UX audit for Arabic right-to-left interfaces is a detailed review of your app or website to check if it works smoothly for Arabic-speaking users. It covers text alignment, layout, navigation, readability, accessibility, and cultural fit. The goal is to make sure the design feels natural for people who read and interact in Arabic.
In the UAE and Saudi Arabia, most users prefer Arabic-first digital experiences. If your design doesn’t match right-to-left reading flow, users get confused and may leave your app or website. A UX audit in UAE and Saudi Arabia ensures your product respects local culture, uses clear Arabic language, and builds trust with the audience.
AI-powered UX audit tools save time and increase accuracy. They automatically scan screens for alignment issues, test readability of Arabic text, predict user behavior with heatmaps, and check accessibility features like screen readers. With AI in Arabic UX audits, businesses get faster results and more reliable insights than manual testing alone.
On average, a mobile app UX audit for Arabic RTL users takes 5–10 business days for a small app and 3–6 weeks for a large or enterprise-level platform. If you use AI-driven UX audit tools, the timeline can shrink significantly; basic reviews may be completed in 2–3 days, while complex apps can be audited in 1–2 weeks instead of several.
Checking design boxes is not always enough for a successful UX audit. Sometimes, respecting culture, ensuring clarity, and making technology truly usable is all that you need for a successful UX audit for RTL interfaces.
This is exactly what you need for a successful UX audit for Arabic right-to-left interfaces for users in the UAE and Saudi Arabia. Plus, AI in UX audits helps save time, reduce errors, and deliver seamless experiences that feel natural and trustworthy.
At the end of the day, users don’t notice when the design is perfect, but they immediately notice when it’s not.
That’s why partnering with experts like Techugo can make all the difference in building apps and websites that connect, engage, and grow in the Middle East market. Sooo…we’re waiting for your call. Book a free call now.
Write Us
sales@techugo.comOr fill this form