Write Us
We are just a call away
[ LET’S TALK AI ]
X
Discover AI-
Powered Solutions
Get ready to explore cutting-edge AI technologies that can transform your workflow!
AI dating apps aren’t just about swiping anymore. They’re now smart platforms that learn how people act, guess who’ll get along, and make things safer and more fun.
Normal apps use simple filters to find matches. AI apps use machine learning, data, and constant studying to find better matches, change things to fit each person, spot fake profiles, and keep people interested for longer.
Things like AI matchmaking, profile scores, guessing compatibility, smart suggestions, stopping scams, and AI chatbots all make building the app take longer and need more tech work.
So, making an AI dating app usually costs 25–50% more than a regular app with the same main stuff.
Budget-wise, a simple AI dating app with basics like signing up, profiles, chats, controls, and basic AI matching usually starts at $40,000 to $70,000.
Better platforms with great matchmaking, profile help, AI checks, and personal advice can cost $80,000 to $140,000.
Big platforms like Ashley Madison or niche apps like Sniffie can go over $180,000–$250,000+, especially if you need to grow, keep data safe, and follow local rules.
This guide looks at what really goes into the cost of making an AI dating app by checking out features, AI parts, tech choices, developer teams, and what you need long term.
Also Read: A Development Guide to Dating App Like Sniffie, Its Cost & Features
In 2025, dating apps made about $9.33 billion. It’s expected to jump to $14.9 billion by 2035. That’s about a 4.8% increase each year, as more people use their phones for dating and spend money on extra features.
Studies show that over 60% of dating apps now use AI to make better matches and give people suggestions they’ll actually like.
Data indicates that about 65% of dating sites using AI see people using the app more and for longer periods.
Plus, 78% of users like apps with AI matchmaking because they think it helps them find better matches.
People want apps to know what they like, give smart suggestions, and match them based on personalities. AI also makes things safer by spotting fake profiles and verifying identities.
Businesses and investors are putting money into AI dating solutions. That is because it makes the app better for users and also helps the company make more money through special features and personal subscriptions.
Since nearly 70% of users are on dating apps every day, along with AI improvements, AI dating apps are a hot area for new ideas and investments in the mobile app world.
There are many kinds of AI dating apps out there, and they differ a lot. The kind of AI model you pick really changes how hard it is to build the app, how many tasks it can do, and how much it will cost in total.
Apps where you swipe left or right, like Tinder, are still what most people think of. People look at profiles and swipe to say if they like someone or not. These apps are starting to use AI to help match people better.
They look at how you swipe, what you seem interested in, and what you like to help find better matches and keep you using the app.
Some even add games to get people more involved. In fact, games make up over half of what people do on these apps in many countries.
AI matchmaker apps do more than just swiping. They utilize complicated methods, look closely at profiles, and give scores based on how well two people might get along to suggest relationships.
Apps like Switch mix AI with detailed question answers and even check things over with people to make a few good introductions.
Users often pay for each match. These apps need more complex AI, like natural language processing and personality analysis.
These apps have features like encrypted messages, places where you can talk privately without showing who you are, ways to check photos and who people are, and controls over how your data is used.
Since almost half of users say that privacy and security are important when they pick a dating service, adding these extra security measures with AI-based tools that identify fraud and moderate content makes the app harder to develop.
There are niche dating apps made for particular groups and interests, such as LGBTQ+ users, religious groups, or people with certain hobbies.
Grindr and Blued, for example, are for LGBTQ+ people. They have their own ways of matching people, social features, and community.
When you cater to these groups, you have to customize the way the app looks and feels, add specialized ways to talk, and utilize recommendation systems that fit the culture.
The kind of app you choose has a clear impact on how much its development would cost. Swipe-based and niche apps can often start with easier AI additions and then grow from there.
Matchmaker and privacy-focused apps usually need deeper data systems, advanced machine learning models, and constant improvements.
Improvements to privacy and personalization, especially when they involve behavioral AI, can greatly increase both the initial and operational costs compared to basic feature sets.
The cost to build an AI-powered dating app is going to depend on a few key factors: how many features you want, which platforms you’re targeting (like iPhones, Androids, or both), and how smart you want the AI to be.
Generally speaking, you can break down the costs into three levels: a basic starter app, a more advanced app with some cool AI features, and a top-of-the-line app built for serious scale.
Also Read: Cost to Develop a Dating App Like Ashley Madison | Techugo

A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is basically the simplest version of your app that still works.
It’s got the core stuff, but the AI is pretty basic.
Think user sign-up, profile creation, simple matching based on rules you set, and maybe some AI-powered suggestions.
You’ll also need a way to manage the app, usually through a basic admin panel.
To save some money, this version is often built using cross-platform tools like Flutter or React Native.
This allows you to use the same code for both iPhones and Android phones.
Expected Cost: $40,000 – $70,000
An MVP is great for testing the waters and getting user feedback before you spend big bucks on more complex AI.
These apps have more advanced AI features.
Think smarter matching that adapts over time, AI that helps users improve their profiles, chat features that suggest ways to rephrase messages, and better recommendations.
Depending on how you want the app to perform, you might go with native development (separate code for iPhones and Androids) or stick with cross-platform.
The admin panel will also be more powerful, with dashboards that show user activity and trends.
Expected Cost: $70,000 – $140,000
The price jump comes from needing to build more sophisticated data models, using Natural Language Processing (NLP) to process text, and adding some predictive features.
These are the big leagues. Apps built for tons of users, high performance, and seriously smart AI.
You’re talking advanced matching algorithms, AI that learns user behavior on the fly, AI-powered tools to detect fake profiles and keep users safe, real-time data analysis, support for multiple languages, and super-complex recommendation engines.
To get the best performance and user experience, these apps are usually built natively for both iPhones and Androids.
Expected Cost: $140,000 – $250,000+
The high cost is driven by complex machine learning systems, robust data security, extensive quality assurance, a dedicated DevOps team, and ongoing support.
The platform you choose matters.
Cross-platform development can save you money upfront, but native development usually delivers better performance, which leads to a smoother user experience.
Adding AI to your dating app will likely increase costs by 20–40% compared to a regular, non-AI dating app.
This is due to the need for training AI models, building data pipelines, continuously improving the AI, and the cloud computing power required to run everything.
A good AI dating app needs two main parts: the Admin Panel and the User Panel.
How these panels are put together affects what users think, how the app makes money, how safe it is, and how easily it can grow.
Plus, it changes how much the whole thing costs to build.
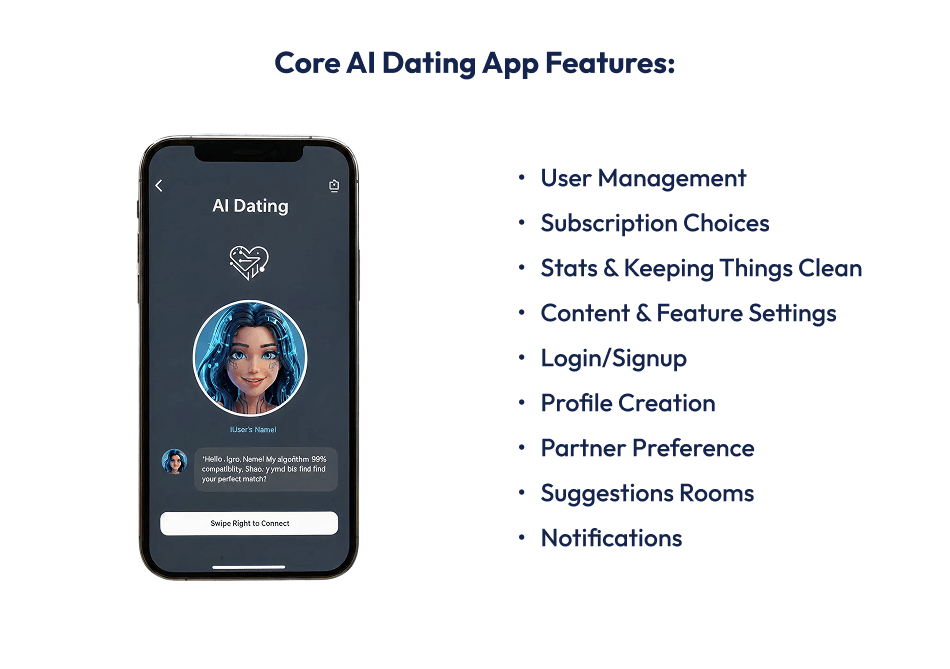
Think of the admin panel as the spot where the app owners can keep everything in good order. They can handle users, make decisions on what content is okay, watch how things are working, and look for ways to increase income.
Some of the key tasks performed by the Admin Panel are as follows:
Admins can look at user information, check if they are legit, stop or kick out users if they cause trouble, keep tabs on what everyone is doing, and fix problems or settle arguments.
The AI can lend a hand by spotting strange activity, fake profiles, or mean stuff automatically, but this can make development a bit more complex and pricey.
If you want to offer different plans, like basic, advanced, or premium, that run for different amounts of time (like a month, three months, six months, or a year), you need things like safe payment methods, a system to keep track of who has what plan, and automatic renewals.
When you add AI to remind people to renew or to guess who might cancel their plan, that increases the costs.
The admin panel can show graphs and reports about things like how people are using the app, how often people are upgrading, how well matches are going, and how many people are sticking around.
This relies on keeping track of actions and moving data around. AI insights are useful, but they also add to what you spend on cloud services and making the app.
Admins need the power to change things like questions, memes, room suggestions, notifications, and new features. Having switches to turn features on and off and test things out makes the whole setup more complicated.
A solid admin panel usually makes up about 20–30% of the total cost to get the app up and running, especially if AI is helping with things like keeping content in check and analyzing data.
The user panel is the user’s view of the app, and it’s what makes users stick around and spend money. Here’s the breakdown of tasks down by user panel:
Getting people safely signed up with email, phone, or social media takes special safety precautions.
The AI looks at things like how complete a profile is, how active someone is, and who they might get along with, then assigns stars. This needs fast data processing and AI smarts.
Asking users what they are looking for and having them answer fun questions gives the AI what it needs to make better matches.
This makes both the user part of the app and the AI smarter.
Helping people meet in groups and having private spaces where they can get comfortable means you need messaging that works in real time, ways to control who gets access, and safety measures to keep identities private.
Things like alerts, pop-ups (like one that appears after a certain amount of talking, asking if the user wants to share their number), AI that rewards messages, voice recording, and chat helpers all make the app more complex.
The user panel usually costs about 50–60% of the total budget, with AI features adding to the cost of backend processing, cloud use, and testing.
Basically, the admin and user panels are where most of the money goes when building an AI dating app.
Unlike traditional dating apps that rely on simple filters such as age, location, or gender, AI matchmaking systems analyze large volumes of user data to predict compatibility with far greater accuracy.
This intelligence is one of the main reasons the cost to develop an AI dating app is significantly higher than that of a standard dating platform.
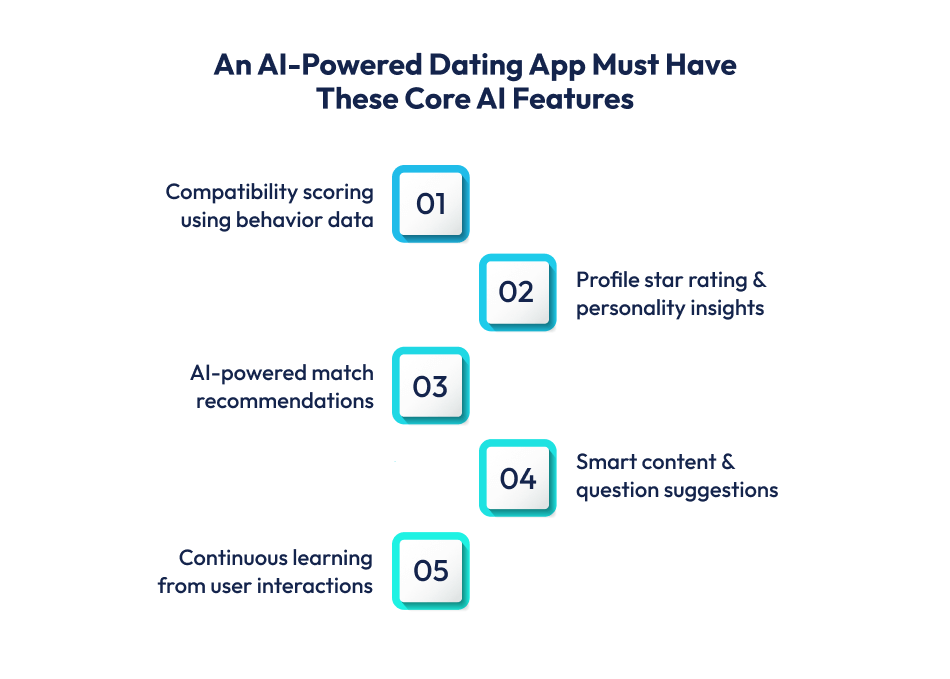
AI matchmaking begins with structured and unstructured data collection. Structured data includes explicit user inputs such as age, interests, lifestyle choices, partner preferences, and answers to onboarding questions or memes.
Unstructured data comes from behavior inside the app, including swipe patterns, time spent on profiles, message frequency, voice interactions, and response styles.
Machine learning models process this data to identify patterns that indicate attraction, compatibility, and long-term engagement potential.
Preference analysis uses AI models to go beyond what users say they want. Over time, the system learns what profiles a user actually engages with, responds to, or ignores. Behavioral tracking continuously refines matchmaking accuracy by adapting to evolving user behavior.
For example, if a user frequently interacts with profiles outside their stated preferences, the algorithm adjusts future recommendations accordingly.
Compatibility scoring assigns a probability or score to each potential match based on multiple weighted factors.
Basic models rely on rule-based scoring or simple collaborative filtering, which is faster to implement and less expensive.
Advanced AI dating app development uses deep learning models, natural language processing for chat analysis, and sentiment detection to evaluate emotional alignment, communication styles, and intent.
From a cost perspective, basic AI matchmaking can add $25,000–$50,000 to the overall cost to develop an AI dating app.
Advanced compatibility engines with real-time learning, NLP-driven insights, and scalable data pipelines can increase development costs by $80,000–$150,000 or more, depending on scale and performance requirements.
Ongoing costs include cloud computing, data storage, model retraining, and monitoring, which typically represent 15–25% of the initial AI investment annually.
AI-driven profile optimization plays a critical role in differentiating an AI powered dating app from traditional swipe-based platforms.
Instead of relying solely on static bios and photos, AI systems actively analyze profile data and user behavior to help users present themselves better and to improve overall match quality.
This layer of intelligence directly impacts engagement, retention, and monetization, but it also adds to the overall cost to develop an AI dating app.
Profile scoring uses machine learning models to evaluate how complete, attractive, and engaging a user profile is.
The system analyzes profile photos, bio text, activity frequency, and interaction outcomes to assign a quality score.
Low-scoring profiles receive automated suggestions such as adding clearer photos, answering more questions, or improving bio clarity.
In advanced AI dating app development, computer vision models assess image quality, lighting, and facial clarity, while NLP models analyze tone, authenticity, and readability of bios.
Modern AI dating apps increasingly rely on personality-driven questions and meme-style prompts to capture deeper emotional and behavioral traits.
AI evaluates response patterns, humor style, emotional language, and consistency across answers to build richer personality vectors.
Over time, behavioral signals such as message length, response speed, and voice note usage further refine personalization.
AI-powered suggestions help users optimize their profiles in real time.
These include recommended profile edits, photo ordering, prompt suggestions, and even paraphrasing assistance to improve clarity or tone.
Some platforms also personalize the home feed by highlighting suggested rooms, compatible communities, or private spaces like snuggle rooms based on user intent and comfort levels.
Implementing AI-driven profile optimization requires integrating multiple AI components, including NLP, computer vision, behavioral analytics, and recommendation engines.
Basic profile scoring and suggestion systems typically add $20,000–$40,000 to development costs.
Advanced personalization features with real-time feedback, image analysis, and adaptive learning can raise costs to $60,000–$120,000+.
Ongoing expenses include cloud processing, model retraining, and continuous data refinement, which should be factored into long-term budgeting when working with a dating app development company.
Messaging is the core engagement layer of any AI dating app, and intelligent communication features significantly influence user retention, safety, and monetization.
Beyond basic real-time chat, modern AI-powered dating apps integrate smart controls and NLP-driven enhancements that shape how and when users interact, directly affecting development complexity and cost.
Also Read: How to Build a Video Chat App Like Mirami: Development Phases, Key Features, and Costs
At the foundation is real-time one-to-one messaging, typically built using WebSockets or cloud-based real-time databases.
This enables instant text delivery, read receipts, typing indicators, and media sharing.
While basic chat functionality is relatively standard, scaling it securely for thousands or millions of users requires robust backend architecture, message encryption, and moderation pipelines.
AI paraphrasing features use natural language processing (NLP) models to help users rewrite messages for clarity, tone, or emotional impact.
This is especially valuable for users who struggle with conversation starters or fear saying the wrong thing.
The AI analyzes sentence intent, sentiment, and context before suggesting improved variations.
Mic recording allows users to send voice notes, adding emotional depth and authenticity to conversations.
From a technical standpoint, this involves audio capture, compression, storage, and secure playback.
Advanced implementations may apply AI-driven speech-to-text, tone analysis, or voice moderation to detect abusive or explicit content.
AI dating apps often include interaction gating mechanisms to enhance safety and drive monetization.
Examples include pop-ups like “Want to reveal phone number?” triggered after a predefined number of messages or interactions.
AI systems track conversation quality, mutual engagement, and behavioral trust signals before enabling such actions.
Natural language processing underpins paraphrasing, moderation, sentiment detection, and interaction analysis.
Basic NLP-powered chat enhancements typically add $15,000–$30,000 to development costs.
More advanced implementations with real-time paraphrasing, sentiment-aware gating, and voice intelligence can increase costs to $40,000–$80,000+, along with ongoing expenses for model usage, retraining, and cloud computation.
Unlike traditional social apps, dating platforms handle sensitive personal data, emotional conversations, and identity-related information, making privacy-by-design and AI-driven safety mechanisms essential rather than optional.
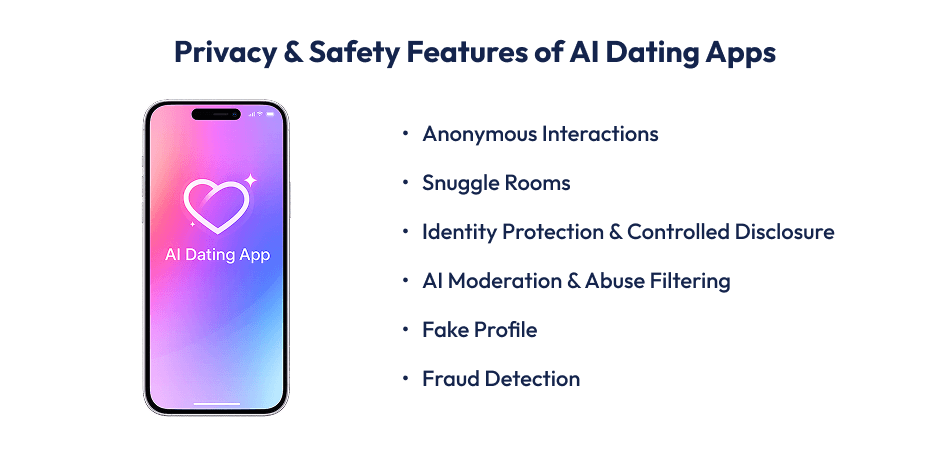
Features such as snuggle rooms are designed to enable private, controlled interactions without immediately revealing a user’s real identity.
In these spaces, users can chat or interact while masking personal details like phone numbers, social handles, or even profile images.
AI systems help manage these environments by monitoring engagement patterns, detecting suspicious behavior, and enforcing interaction limits.
From a development perspective, anonymity requires additional layers of user abstraction, session management, and data segregation, increasing backend complexity and testing effort.
AI dating apps increasingly rely on progressive disclosure models, where sensitive information is unlocked only after trust signals are established.
Examples include phone numbers that reveal pop-ups after a certain number of meaningful interactions or mutual consent.
AI evaluates factors such as conversation tone, reciprocity, response frequency, and behavioral consistency before allowing disclosures.
AI moderation is a critical safety layer for filtering inappropriate content, harassment, hate speech, and explicit material in real time.
Natural language processing models analyze messages for toxic language, coercion, or policy violations, while computer vision can be used to scan profile images or shared media.
Advanced systems also detect grooming patterns or repeated boundary violations. Depending on sophistication, AI moderation modules can add $25,000–$70,000+ to development costs, along with ongoing model monitoring and updates.
Fake profiles and scams undermine platform credibility and user safety.
AI-driven detection systems analyze profile completeness, image authenticity, behavioral anomalies, and network patterns to flag or block suspicious accounts.
Techniques such as face recognition (to detect reused images), device fingerprinting, and activity clustering help reduce fraud at scale.
Dating apps must comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and regional privacy laws.
Compliance and security implementation typically add 10–20% to total development cost but are critical to avoiding legal exposure and maintaining user trust.
Together, privacy, safety, and AI trust systems transform dating apps into secure platforms where users feel protected enough to engage meaningfully.
Suggested rooms and group-based interactions play a crucial role in increasing engagement and retention in AI-powered dating apps. These features significantly extend session duration and encourage repeat usage.
Suggested rooms function as themed group spaces centered around shared interests, lifestyles, or relationship intentions.
Examples include fitness enthusiasts, late-night chat rooms, introvert spaces, LGBTQ+ safe rooms, or region-based communities.
AI determines which rooms appear on a user’s homepage by analyzing profile attributes, answered questions, interaction history, behavioral signals, and engagement patterns.
Machine learning models continuously refine recommendations by tracking which rooms users join, how long they stay active, and whom they interact with.
AI personalizes the homepage by prioritizing suggested rooms, active matches, trending discussions, and recommended interactions based on individual user behavior.
New users may see onboarding-friendly rooms, while active users are shown high-engagement groups aligned with their interests.
Developing personalized home feeds involves event tracking, real-time analytics, and content ranking pipelines, contributing to higher development and infrastructure costs.
AI enhances notification effectiveness by optimizing timing, frequency, and messaging based on user behavior.
Instead of generic alerts, users receive contextual nudges such as “A new room matches your interests” or “People from your favorite group are active now.”
AI models predict the best moments to send notifications without causing fatigue, improving open rates and re-engagement.
By combining suggested rooms, personalized homepages, and smart notifications, AI significantly boosts session time and long-term retention.
From a cost perspective, these engagement systems typically add $20,000–$60,000+ depending on AI depth, real-time personalization needs, and scalability requirements, but they deliver measurable gains in user lifetime value and platform stickiness.
Also Read: Pet Dating App Development: Market Opportunities, Features, Cost, and Business Models
Choosing the right technology stack is a foundational decision when building an AI dating app, as it directly affects development cost, performance, scalability, and long-term maintenance.
AI-powered dating apps require a more robust and flexible stack than traditional apps due to real-time interactions, heavy data processing, and continuous model learning.
The frontend layer focuses on user experience, responsiveness, and real-time interactions.
Most AI dating apps are built using native technologies such as Swift (iOS) and Kotlin (Android) for high performance and smooth animations.
To reduce time-to-market and cost, many teams opt for cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native, which allow a single codebase for both platforms.
The backend is the core engine that handles user authentication, matchmaking logic, messaging, notifications, subscriptions, and admin controls.
Popular backend technologies include Node.js, Python (Django or FastAPI), and Java (Spring Boot).
AI dating apps typically rely on microservices architecture to scale individual components independently, such as chat, recommendations, and notifications.
This approach improves reliability but increases initial setup and DevOps costs.
AI dating apps manage large volumes of structured and unstructured data, including profiles, chats, preferences, and behavioral events.
Relational databases like PostgreSQL or MySQL are commonly used for transactional data, while NoSQL databases such as MongoDB or Cassandra support real-time feeds and chat systems.
For AI workloads, data lakes and analytics storage (e.g., BigQuery, Redshift) are often added, increasing infrastructure complexity and cost.
Machine learning models are typically built using TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Scikit-learn for matchmaking, personalization, and moderation.
Natural language processing for AI paraphrasing and chat moderation may leverage APIs from providers like OpenAI, Google Cloud AI, or AWS AI services.
While APIs reduce development time, usage-based pricing can significantly impact ongoing operational costs at scale.
Most AI dating apps run on cloud platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure.
Cloud services support autoscaling, real-time processing, and AI workloads but require careful cost optimization.
Understanding the cost to develop an AI dating app requires breaking the project into its core components.
Unlike traditional dating platforms, AI-powered dating apps involve advanced data processing, machine learning models, and continuous optimization, all of which significantly influence total investment.
Below is a realistic breakdown of where the budget goes when estimating the cost to build a mobile app in the dating space.
UI/UX design lays the foundation for user trust, engagement, and retention.
For AI dating apps, design goes beyond screens and visuals, it includes interaction flows for matchmaking, privacy-first features like snuggle rooms, pop-ups for number reveal logic, and intuitive onboarding.
Wireframing, prototyping, visual design, and usability testing typically account for 15–20% of total development cost.
For an MVP, UI/UX costs usually range between USD 8,000–20,000, while more advanced, animation-heavy, and highly personalized interfaces can reach USD 30,000–45,000+.
Backend development covers user authentication, profile management, subscription plans (30/90/180/365 days), messaging systems, notifications, admin controls, analytics, and scalability infrastructure.
AI dating apps also require real-time data pipelines to support matchmaking and personalization.
Backend development typically consumes 30–40% of the total budget, with costs ranging from USD 25,000–60,000 for MVPs and USD 70,000–120,000+ for advanced apps with complex logic, integrations, and microservices architecture.
AI is what differentiates modern dating platforms and significantly impacts the cost to develop an AI app for dating.
Key AI components include matchmaking algorithms, profile scoring, behavior analysis, AI paraphrasing, fake profile detection, moderation systems, and recommendation engines.
Basic AI implementations using pre-trained models and third-party APIs may cost USD 20,000–40,000, while custom-built AI engines with continuous learning, personalization, and advanced NLP or computer vision can range from USD 60,000–150,000+.
Ongoing AI costs for cloud compute, retraining, and data storage typically add 15–25% annually on top of initial AI development.
AI dating apps require extensive testing across devices, platforms, and edge cases, including security testing, performance testing, AI model validation, and abuse scenario testing.
QA usually represents 10–15% of total development cost, ranging from USD 8,000–25,000, depending on app complexity and compliance requirements.
Deployment includes app store submissions, cloud setup, monitoring tools, and post-launch support. These costs typically fall between USD 3,000–10,000.
Regionally, total development costs vary widely. US-based teams may quote USD 120,000–250,000+ for full AI dating apps, while teams in India or Eastern Europe often deliver similar scopes in the USD 50,000–120,000 range, making regional selection a critical cost decision.
Many founders budget only for initial development and underestimate the true cost of running an AI dating app. Long-term expenses often determine whether the product can scale sustainably.
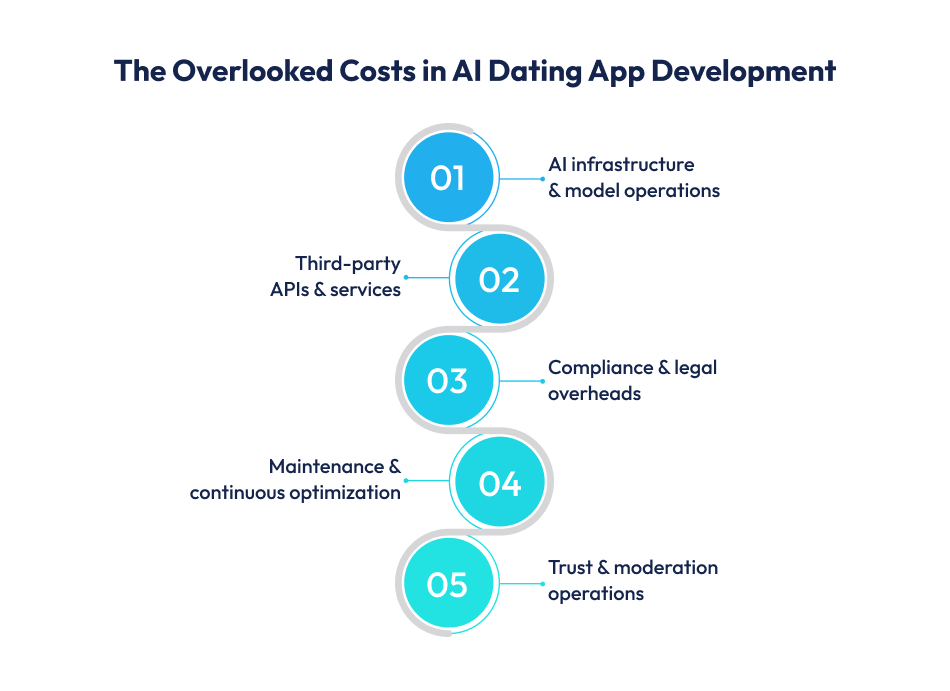
AI matchmaking, profile scoring, NLP moderation, and recommendations require GPU hosting, model inference, data pipelines, and periodic retraining. As usage grows, these costs typically add 15–30% annually to operational spend.
SMS/OTP, email, push notifications, payment gateways, maps, media storage, and moderation APIs seem inexpensive individually. At scale, they can collectively cost USD 2,000–6,000+ per month.
GDPR, age verification, consent management, and data residency rules require legal reviews, audits, and engineering updates. Multi-region apps may spend USD 8,000–20,000+ over time on compliance.
AI systems evolve with user behavior. Ongoing bug fixes, model tuning, and UX improvements usually consume 15–25% of the original development cost annually.
Even with AI moderation, human review teams, appeals handling, and fraud prevention add unavoidable operational overhead as the platform grows.
Developing an AI dating app can quickly become expensive if scope, infrastructure, and AI complexity are not controlled from the start. Here are some simple ways to reduce and optimize costs.
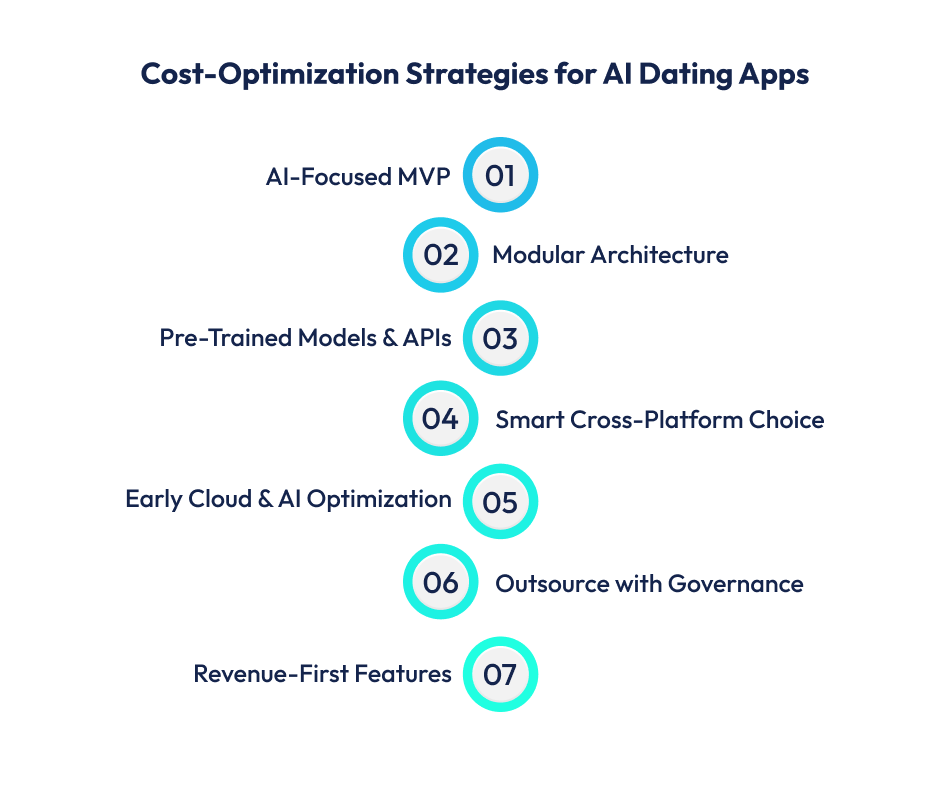
The most effective way to manage cost is to begin with a well-defined MVP. Early-stage apps do not need deep-learning-heavy models.
Lightweight machine learning or rule-assisted AI can validate demand and user behavior first, often reducing initial development costs by 30–40%.
Matchmaking, NLP chat tools, moderation, and recommendation engines should be loosely coupled rather than tightly embedded into core logic.
This allows individual AI systems to be upgraded, replaced, or scaled without rebuilding the entire platform, significantly lowering long-term engineering costs.
Using pre-trained NLP models, recommendation engines, and moderation APIs allows faster deployment and lower upfront spend.
Fine-tuning should be reserved for features that directly differentiate your AI powered dating app. This approach can save USD 20,000–50,000+ during early development.
Using cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native reduces duplicated effort across iOS and Android.
A shared codebase speeds up development, simplifies QA, and lowers ongoing maintenance costs.
Avoid over-provisioning servers or GPUs. Auto-scaling cloud infrastructure, optimized inference schedules, and batch processing can drastically reduce hosting and AI computation costs.
Partnering with an experienced mobile app development company using offshore or hybrid teams can reduce costs by 40–60%.
Clear documentation, defined milestones, and strict scope control are essential to prevent rework and budget overruns.
Focus early development on AI features tied to monetization such as match quality, profile optimization, boosts, and premium insights.
Delaying experimental or low-impact features ensures capital is spent where it drives measurable returns.
Unlike standard mobile apps, AI-powered dating platforms must be tested not only for functional correctness but also for model accuracy, bias, and real-world behavior.
Functional testing ensures that all primary user and admin workflows operate reliably across devices and platforms.
This includes onboarding, login and signup, profile creation, matchmaking logic, messaging, subscriptions, notifications, payment flows, and admin panel controls.
Performance testing evaluates how the AI dating app behaves under real-world usage conditions.
This includes peak-time matchmaking, real-time chat concurrency, push notification delivery, and database response times.
AI-specific QA focuses on validating matchmaking relevance, compatibility scoring accuracy, and recommendation consistency.
Testing also covers bias detection, edge cases, and model behavior as user data evolves. NLP-based features such as AI paraphrasing, content moderation, and abuse filtering require separate validation to ensure context-aware and safe interactions.
Testing and quality assurance typically account for 10–15% of total development cost.
Budgets range from USD 8,000–20,000 for MVP AI dating apps and can extend to USD 25,000–40,000+ for advanced platforms with complex AI models, compliance requirements, and large-scale deployments.
AI dating apps handle sensitive personal data, private conversations, and behavioral insights. Strong security is essential to protect user trust and prevent legal and reputational risks.
Apps must comply with GDPR, CCPA, and local data protection laws. These rules affect how user data is collected, stored, processed, and deleted, influencing overall development and maintenance costs.
Key protections include end-to-end encryption, OAuth 2.0–based authentication, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control for admin panels. These reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data leaks.
Secure storage of chats, voice data, preferences, and AI training datasets requires robust cloud infrastructure and monitoring systems.
Security and compliance typically add USD 10,000–30,000 upfront, with ongoing costs of 5–10% annually for audits and monitoring.
AI dating apps rely on layered monetization models designed to maximize lifetime value while keeping entry barriers low.
The most common approach is subscription-based pricing, typically structured into basic, premium, and pro tiers, with durations such as 30, 90, 180, or 365 days.
Basic plans often unlock limited matches or interactions, while higher tiers provide unlimited likes, advanced filters, profile visibility boosts, and priority matchmaking.
Boosts and add-ons act as high-margin revenue drivers.
These include profile boosts, super likes, read receipts, message prioritization, and temporary access to premium rooms or anonymity controls.
Because these features are event-driven, they generate impulse purchases and significantly increase average revenue per user.
AI further amplifies monetization through premium intelligent features.
AI-powered match insights, personality analysis, smart conversation starters, compatibility scoring, and profile optimization tools are commonly placed behind paywalls.
Personalized pricing, powered by AI usage patterns and engagement data, also enables dynamic offers and targeted upsells.
Post-launch costs are a critical part of AI dating app development and often determine long-term success. Once the app is live, ongoing hosting and infrastructure expenses increase as user activity grows.
Cloud costs scale with concurrent users, real-time messaging, media storage, and AI inference workloads, making infrastructure planning essential from day one.
AI-powered dating apps also require continuous model retraining and optimization. Matchmaking algorithms, recommendation engines, moderation systems, and personalization models must be updated regularly using new user data to maintain accuracy and relevance.
Beyond AI, feature updates and platform upgrades add to maintenance costs. Regular OS updates, security patches, UI improvements, and performance optimizations are necessary to retain users and remain competitive.
Most businesses allocate 15–25% of the initial development cost annually for maintenance, scaling, and AI refinement.
Planning these costs early ensures stable growth, consistent user experience, and predictable long-term ROI.
Building an AI dating app is a high-impact investment driven by feature scope, AI complexity, platform choices, compliance needs, and long-term scalability. From MVPs to enterprise-grade platforms, realistic budgeting around AI modules, hidden costs, cloud infrastructure, and post-launch optimization is essential to avoid overruns and ensure sustainable growth. Clear planning and the right technical decisions significantly reduce risk while improving time to market.
Partnering with a reliable mobile app development company makes this process more predictable. Techugo helps businesses design and build AI-powered mobile applications with scalable architectures and cost-efficient development strategies. With a strong focus on MVP planning, AI integration, and future-ready technology, Techugo enables teams to launch robust products built for long-term growth.
Write Us
sales@techugo.comOr fill this form